An Arctic blast plunged into the southeastern United States on Sunday, January 19, arriving simply in time for the on-average coldest stretch of the 12 months. It introduced record-breaking low temperatures and fueled a winter storm that dropped historic snowfall for components of the South.
Temperatures had been properly under freezing (blue) throughout a lot of the U.S. Southeast on the morning of January 22, 2025. NOAA Local weather.gov picture, based mostly on RTMA/URMA knowledge.
On January 22, Baton Rouge, LA, made it to 7 levels, which is the airport’s coldest temperature since data started in 1930. (Earlier, pre-airport, knowledge from Baton Rouge confirmed a two-day chilly snap in 1899 when the temperature dropped to 2 levels on February 13 and seven levels on February 14.) Lafayette, LA, was even colder at 4 levels, a document low since data started in 1893. Lastly, New Iberia, LA, noticed 2 levels, making it the location’s record-coldest temperature since its creation in 1948.
[Corrections, 02/04/25: A reference to temperature at New Orleans Lakefront in the original version of the article has been removed after additional review of the record showed large stretches of missing data. The text has also been edited to state that the Baton Rouge Airport record began in 1930, not 1935, as originally stated, and that the 2025 temperature of 7 degrees was an airport location record, but not the coldest ever observed for a station at that location.]
Because the record-breaking chilly set in, so did the historic snowfall. Texas noticed the primary snowflakes of the storm on the night time of January 20 earlier than the storm started its trek eastward. One of the notable data from the state was the 4.5 inches that fell within the Beaumont-Port Arthur Space on January 21, making it the snowiest day for the location because it started its data in 1901.
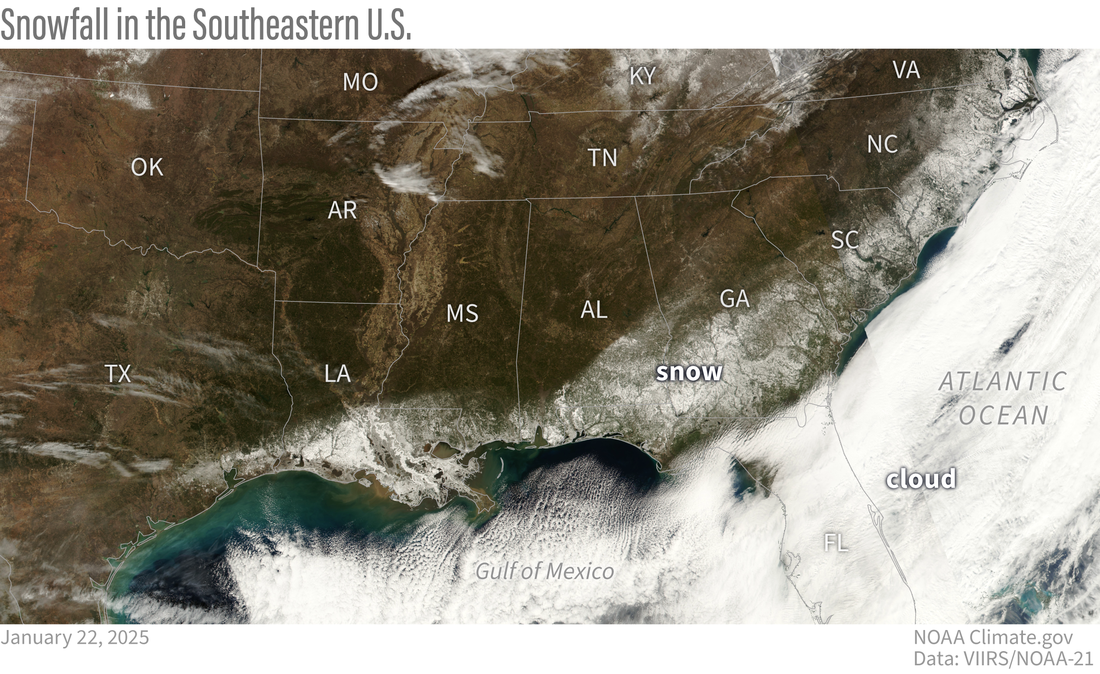
After the storm clouds cleared on January 22, 2025, satellites captured an uncommon sight: a swath of snow arcing across the Gulf Coast and the Atlantic Southeast. Local weather.gov picture based mostly on NOAA-21 satellite tv for pc knowledge from the VIIRS sensor.
Because the storm tracked eastward, it continued to make historical past in Louisiana on each January 21 and 22. The Nationwide Climate Service workplace in Lake Charles, LA, issued its first blizzard warnings ever for parts of the state. On January 21, Baton Rouge recorded 7.6 inches, making it the location’s snowiest day since data started in 1892 whereas New Orleans noticed its snowiest day since data started in 1948 with a complete of 8.0 inches. On January 22, Thibodaux additionally noticed its snowiest day since data started in 1893, with 8.5 inches of snow. Cellular, AL, hit a document snowfall of seven.5 inches on January 21, essentially the most because the website’s creation in 1881. Lastly, 10.0 inches was recorded close to Pensacola, FL, on January 21, difficult the document for the snowiest day ever recorded within the state of Florida. [Correction, 02/04/2025: Mention of a record 4 inches of snow in Fernandina Beach, FL, was removed following an update to the reported totals for the station.]

Tons of of stations throughout the South and Southeast set new snowfall data between January 20 and 22, 2025. This map reveals stations that set a brand new document for 1-day snow totals throughout the three-day interval. Stations the place even a hint of snowfall was a brand new document are indicated by the lightest blue dots. Nearer to the coast—nearer to the moisture supply—some stations set data with quantities nearer to 10 inches (darkish purple). NOAA Local weather.gov picture based mostly on preliminary snow knowledge compiled by Jessica Spaccio, NOAA Northeast Regional Local weather Heart.
In truth, some areas in Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida collected 10.0 or extra inches of snow from the storm. With these totals, these websites have recorded extra snow thus far this winter season than many areas far to the north, together with Chicago, IL!
The uncommon atmospheric arrange for a southern “lake impact” snowstorm
Unusually chilly and dry air, originating from the Arctic, was in place throughout a lot of the Gulf Coast previous to the start of the winter storm that buried a lot of the world in inches of snow. By January 20, 2025, a big trough within the higher ambiance (often known as a dip within the jet stream) was pushing south and east throughout a lot of the central U.S., stretching from the Nice Lakes all the way in which all the way down to the Gulf Coast.
Forward of this trough, to the east, moisture from the Gulf of Mexico was drawn northward, not solely over the southern states, but additionally all through the atmospheric column. On the identical time, a floor low developed throughout the central Gulf of Mexico (forward of the trough), reinforcing moisture movement northward over the Gulf Coast states. This aided in saturating the chilly (properly under freezing), dry air that was already in place, finally resulting in snowfall reaching the bottom.
The collision of Gulf moisture with such chilly, dry air was like a lake-effect snowstorm throughout the South. The Nationwide Climate Service workplace in Cellular, Alabama, estimated an “unusually excessive snow to liquid ratio” starting from 10:1 to fifteen:1 throughout the peak of the occasion, which resulted in “drier, fluffier snow… that’s rather more environment friendly at accumulating.” Any such powdery snow is rather more generally present in mountain areas than at low elevation, southerly latitudes.
Stratospheric polar vortex connection? What about local weather change?
The southward dip within the jet stream that introduced this chilly air outbreak was aligned with a stretching occasion within the stratospheric polar vortex. Some latest analysis has linked these polar vortex stretching occasions to local weather change. In keeping with NOAA polar vortex professional Amy Butler, the speculation is “that melting Arctic sea ice [due to human-caused warming] may elongate the form of the polar vortex and encourage a southward-shifted jet stream and extra Arctic blasts. Nonetheless, the proof for this connection is blended, and the science stays unsettled.”
On the subject of the affect of local weather change on winters within the South and the remainder of america, the principle factor to know is that excessive chilly and snow—even occasional new data—aren’t incompatible with warming winters general. Chilly extremes nonetheless happen, however the odds are lowering over time.
